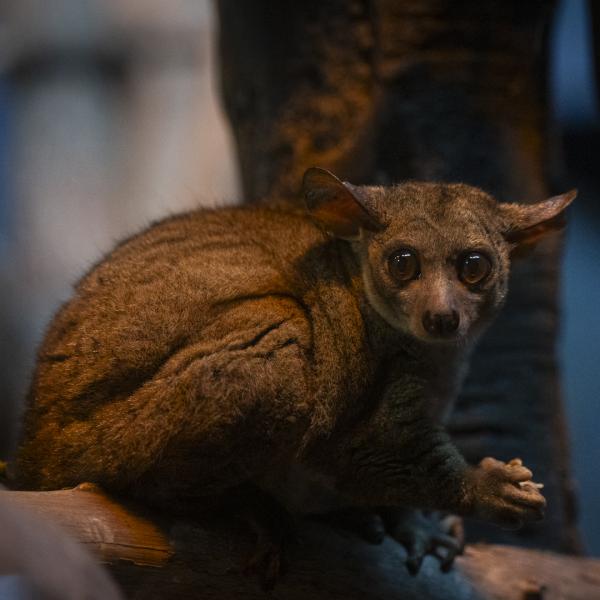
These small nocturnal mammals are also known as bush babies.
Galagos spend most of their lives in trees. In fact, in Afrikaans, they’re also known as “nagapies,” which translates directly to “night monkeys.”
Scientific Name: Otolemur garnettii
Conservation Status: Least Concern
Size: Body length is approximately 10 inches, with a tail length of nearly 14 inches
Weight: Between 1.5 and 2 lbs.