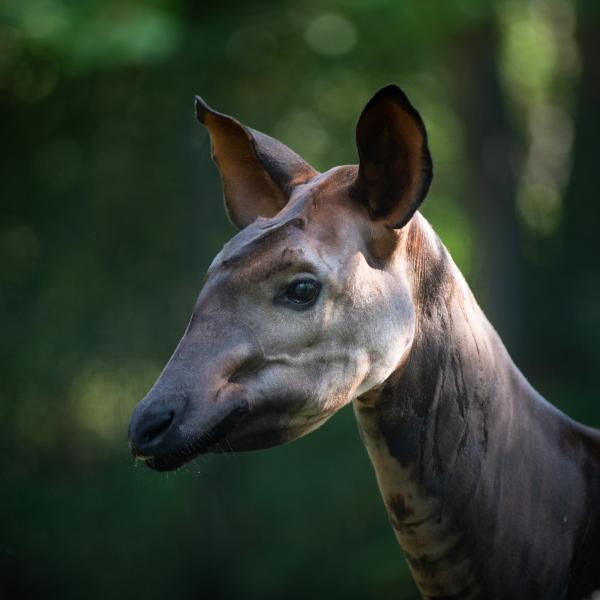
Although it resembles the zebra, the okapi is most closely related to the giraffe. They share many of the same characteristics, including a long, prehensile tongue for stripping leaves from branches and grooming.
Okapis are only found in the dense Ituri rainforest of the northeastern Democratic Republic of the Congo. Their secretive nature and dense forest habitat make them very difficult to observe. In fact, okapi are so elusive that they were not known to the Western world until the 20th century.
Scientific Name: Okapia johnstoni
Conservation Status: Endangered
Size: 5.8 to 6 ft. tall
Weight: 500 to 700 lbs., with females generally larger than males
Median Life Expectancy: 17 years