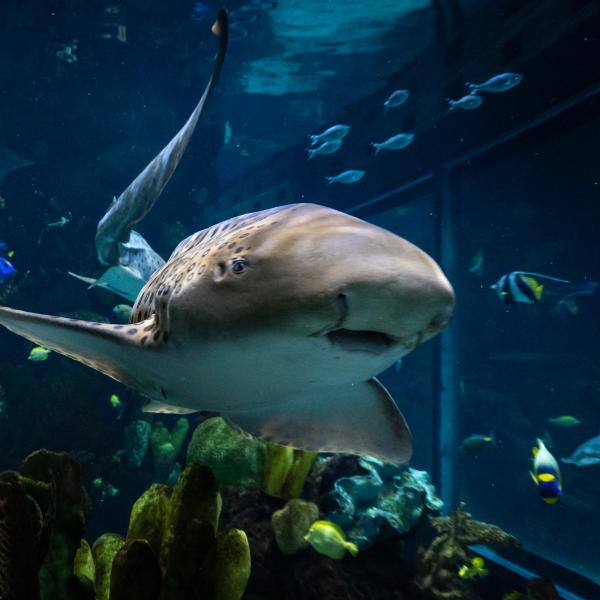
Juvenile sharks are dark brown with stripes that look like a zebra's pattern. As they grow up, adult sharks become tan and have brown spots that are like a leopard’s.
Because of these unique appearances, the species has two different common names. In the United States, people often call them zebra sharks, while in Australia, where these sharks are frequently found, they are referred to as leopard sharks.
At the Columbus Zoo, we’re dedicated to the conservation of sharks like the zebra shark, specifically through our participation in The Association of Zoos and Aquariums' (AZA) Saving Animals from Extinction (SAFE) program.
Located in the Shores & Aquarium Region
Scientific Name: Stegostoma fasciatum
Conservation Status: Endangered
Size: Average length is 5 to 7 feet, with the longest being 11.5 feet
Weight: 45 to 80 pounds
Median Life Expectancy: Median Life Expectancy: cannot be determined